7 : Topology
Topology
The topology is very important to maintain the geographic dataset in ArcGIS. This chapter will help us to learn how to apply a topology to the geodatabase.
The topology is a set of rules coupled with some editing techniques to ensure the accuracy of the model.
We have to ...
- Display the Topology Toolbar;
- In the ‘Customize’ menu, choose ‘Toolbars’ and Topology.
Let's start ...
- Create a topology
- Define rules
How it works…
- In ArcCatalog, right click the feature dataset to which we want to add a topology, choose ‘New’ then ‘Topology’.
- In the ‘New Topology Window’, click ‘Next’. Choose a name for the topology (Gov_Topology) and specify the cluster tolerance then click ‘Next’.
- Select the feature classes that will participate in the topo
- logy. Click ‘Next’.
- Set the coordinate accuracy ranks for each feature class in the topology.
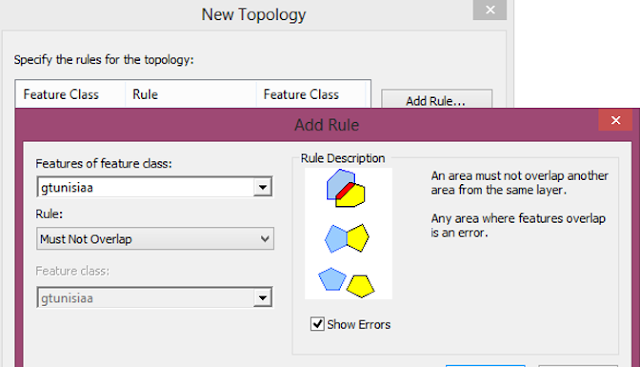
- Now choose a series of topology rules to structure the spatial relationships between features and to control and validate how features share geometry
- We can choose from a list of many topology rules, depending on the relationships we want to set.
- Polygon rules :
- Must Not Overlap: Features in this rule must not overlap another feature in the same layer.
- Must Not Have Gaps: If we have a data that must completely cover an area, we can use this rule to display an error when there is a voids within a single polygon or between adjacent polygons.
- Must Not Overlap With: This is used when we have two layers or more! We select this rule when we like to display errors of features which overlap another features in another layer.
- Must Be Covered By Feature Class Of: Not like the previous rule, features should overlap another features in another layer. If any area do not cover another one, this will display an error.
- Must Be Covered By: This rule display an error when an area of one layer is not completely covered by an area of another layer.
- Boundary Must Be Covered By: Boundaries of polygon features must be covered by lines in another feature class.
- Area Boundary Must Be Covered By Boundary Of: The boundary area of the first feature should cover the boundary area of the second feature.
- Contains Points: This is used when we need to verify that polygons have at least one associated point. Points of one layer should be within the polygons of the other layer. If these points are on the boundary, this should not be an error.
- Contains One Point: Just like Contains Points rule, but this one require that polygons should contain exactly one point.
- Line rules :
- Must Be Larger Than Cluster Tolerance: require that a feature does not collapse with another one.
- Must Not Overlap: This is used to avoid duplication of lines. Lines should not overlap other lines in the same feature class.
- Must Not Intersect: Lines should not cross or overlap each other.
- Must Not Have Dangles: A dangle, is a non-connection between an end point and a line. Lines should touch each other at both end points.
- Must Not Have Pseudonodes: Line features must connect to two other line features at each end.
- Must Not Intersect Or Touch Interior: Requires that a line in one feature class must only touch other lines of the same feature class at endpoints
- Must Not Overlap With: This rule is used when we have two or more layers, not like ‘Must Not Overlap’ rule which is used for one layer. Feature class must not overlap with line features in another feature class.
- Must Be Covered By Feature Class Of: Lines from one feature class must be covered by the lines in another feature class.
- Must Be Covered By Boundary Of: Lines must be covered by the boundaries of area features.
- Endpoint Must Be Covered By: The endpoints of line features must be coverd by point features in another feature class.
- Must Not Self Overlap: Line features should not overlap themselves.
- Must Not Self Intersect: Line features must not cross or overlap themselves.
- Must Be Single Part: Lines must have just one part.
- Point rules :
- Must Be Covered By Boundary Of: A point must be covered by a boundary of a polygon.
- Must Be Properly Inside Polygons: Points must all be covered by an area feature.
- Must Be Covered By Endpoint Of: Points in one feature class must be covered by the end points of another feature class.
- Must Be Covered By Line: Points in one layer, must be covered by lines from another layer.
- Click on ‘Next’ then ‘Finish’.
- To validate the topology that we have created, click on ‘Yes’ in the ‘New Topology’ dialog Box.
- Click ‘Next’ and ‘Finish’
- To remove a feature class, right click the topology, choose ‘Properties’ then click ‘Feature Classes’ tab. Select the feature class we want to remove and click ‘OK’.
- To rename a topology, right click on it, then choose ‘Properties’, ‘General’ tab, and rename it then click ‘OK’.
***
We can create a topology using the geoprocessing tools.
There are many tasks to work with rules within a topology. You can do the following:
- Add or remove rules from an existing topology.
- Save rules as a rule set file that can be shared and reused.
- View rule descriptions and diagrams.

0 Response to "7 : Topology"
Post a Comment